This evaluation compares a 19TB high-performance storage system, assessing maxRAID against conventional RAID solutions like MD RAID, Xinnor, and GRAID. While conventional RAID depends on high-endurance SSDs for longevity, maxRAID delivers optimized performance with lower-endurance drives. By leveraging data compression and advanced optimizations that reduce wear, maxRAID ensures consistent, long-lasting performance. We assume 20% data compressibility for general-purpose data.
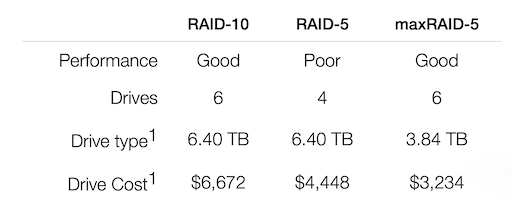

maxRAID-5 delivers better performance at half the cost of RAID-10. While RAID-5 may seem similar upfront, its poor performance often makes it unacceptable, and rapid media wear leads to costly long-term expenses. With maxRAID’s advanced wear optimization, you save on costs and can use lower-cost drives—without sacrificing performance.

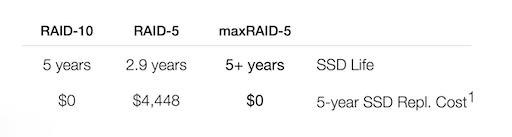
1: Based on Micron 3 DWPD 6.4TB $1112, maxRAID uses 1 DWPD 3.84TB $539. Drive costs only; excludes host system and software licenses.
How does maxRAID work
maxRAID revolutionizes storage with advanced Host FTL architecture. It optimizes data flow, converting random writes into efficient, sequential patterns, compressing data in real-time, and reducing SSD wear. The result? Lower latency, more usable capacity, and sustained performance that outlasts traditional RAID systems.
Fewer drives, more capacity

Reduce Day-1 and long-term costs.

Extend SSD lifespan with peak performance
Download Our White Paper
Please provide your email address to receive the link to download the white paper. Your information will help us keep you updated with the latest insights and innovations.


